1. Introduction
For many women facing fertility challenges, ovarian stimulation is a crucial part of assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as In vitro fertilization (IVF). This process helps to stimulate the ovaries, enabling them to produce multiple eggs, which can then be fertilized to create embryos. Understanding ovarian stimulation is vital for anyone considering fertility treatments, as it significantly impacts the chances of a successful pregnancy.
In this article, we’ll explain what ovarian stimulation is, how it works, and why it’s an essential step in fertility treatments.
2. What is Ovarian Stimulation?
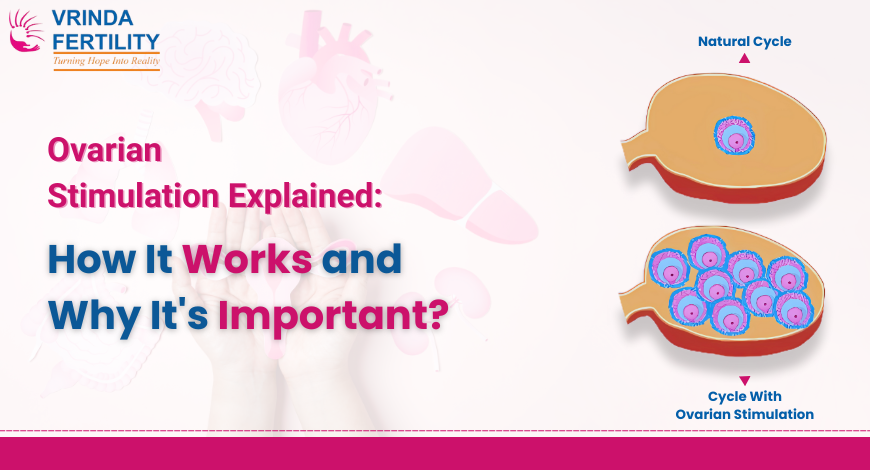
Ovarian stimulation is a medical procedure used in fertility treatments to encourage a woman’s ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Normally, a woman’s body produces one egg each menstrual cycle, but with ovarian stimulation, fertility specialists use medications to prompt the ovaries to produce several eggs. This increases the chances of having multiple viable eggs for fertilization, improving the likelihood of success in procedures like IVF.
By stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, ovarian stimulation plays a pivotal role in ensuring that there are enough high-quality eggs available for fertilization, which is particularly important when a woman has issues with egg production or if she is undergoing IVF or egg freezing.
3. How Ovarian Stimulation Works
Step 1: Initial Consultation and Hormone Testing
The process of ovarian stimulation begins with an initial consultation with a fertility specialist. During this appointment, the doctor will review the patient’s medical history, perform physical exams, and recommend necessary hormone tests. These tests provide insights into the patient’s ovarian reserve and general fertility health, allowing the specialist to tailor the treatment plan based on individual needs.
Step 2: Hormonal Medications
Ovarian stimulation typically involves the use of injectable hormonal medications, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which encourage the ovaries to produce eggs. These hormones are administered over a period of several days and work by stimulating the follicles within the ovaries to mature and prepare for ovulation.
FSH is particularly important for stimulating the growth of multiple follicles, while HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is often used to trigger ovulation once the eggs are mature enough for retrieval.
Step 3: Monitoring and Adjustments
Throughout the ovarian stimulation cycle, regular monitoring is essential to ensure that the ovaries are responding to the medications as expected. This monitoring typically involves ultrasounds and blood tests to check hormone levels, follicle size, and ovarian response. Based on these results, the fertility specialist may adjust the medication dosage to optimize the response and prevent complications such as ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS).
Step 4: Triggering Ovulation
Once the eggs are sufficiently matured, the final step is to trigger ovulation. This is typically done using an HCG trigger shot. The shot stimulates the ovaries to release the eggs, making them ready for retrieval. Timing is crucial in this step to ensure that the eggs are retrieved at the optimal moment.
4. The Benefits of Ovarian Stimulation
Ovarian stimulation offers several key benefits, especially for women undergoing IVF or fertility treatments:
- Increased chances of success with IVF: By producing multiple eggs, ovarian stimulation boosts the chances of retrieving a viable egg for fertilization.
- Egg freezing: For women who wish to delay pregnancy, ovarian stimulation enables the collection and freezing of eggs for future use.
- Enhanced fertility for women with certain conditions: Women with conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), low ovarian reserve, or unexplained infertility can benefit from ovarian stimulation, as it improves the chances of egg retrieval.
Ovarian stimulation plays a central role in ensuring that fertility treatments, such as IVF, have the best possible chance of success.
5. Risks and Side Effects of Ovarian Stimulation
As with any medical treatment, ovarian stimulation comes with certain risks and side effects. While the vast majority of women experience mild or moderate side effects, it’s essential to be aware of them.
Common Side Effects:
- Bloating and discomfort due to the enlarged ovaries.
- Mood swings due to hormonal changes.
- Headaches and nausea.
- Fatigue and changes in appetite.
Serious but Rare Risks:
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): This is a rare but serious condition where the ovaries become swollen and painful. In extreme cases, OHSS can cause fluid buildup in the abdomen or chest, which requires medical intervention.
Fertility specialists closely monitor patients during the ovarian stimulation process to minimize these risks and ensure a safe and effective outcome.
6. The Role of Ovarian Stimulation in IVF Treatments
In IVF treatments, ovarian stimulation is an integral step that directly affects the success of the procedure. By stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, the chances of retrieving viable eggs for fertilization are significantly increased.
Once the eggs are retrieved, they are fertilized in the laboratory, and the resulting embryos are monitored for development. The best quality embryo is then selected for transfer into the woman’s uterus. The more eggs that are retrieved and successfully fertilized, the greater the chances of having a healthy embryo for implantation.
7. Success Rates and Considerations
Ovarian stimulation has a direct impact on the success rates of IVF. The number of eggs retrieved, the quality of those eggs, and the woman’s age all influence the likelihood of a successful pregnancy.
Women who are younger, with healthy ovarian reserves, typically have higher success rates with ovarian stimulation. However, the process can still be successful for women who are older or have conditions like PCOS, as ovarian stimulation can help overcome fertility obstacles.
8. Alternatives to Ovarian Stimulation
While ovarian stimulation is a common and effective option, there are alternatives for women who may not be candidates for stimulation or those who prefer other treatments:
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): IUI is a less invasive treatment that involves placing sperm directly into the uterus. It can be used with or without ovarian stimulation.
- Natural Cycle IVF: This approach uses no medications to stimulate the ovaries and relies on the body’s natural cycle to produce one egg. It is generally used for women with good ovarian reserve and regular cycles.
Each option has its pros and cons, and the right treatment plan depends on the individual’s specific fertility challenges and goals.
9. Conclusion
Ovarian stimulation is a vital part of fertility treatments, especially in IVF. It enhances the chances of a successful pregnancy by helping the ovaries produce multiple eggs, which increases the chances of fertilization. While ovarian stimulation comes with some risks, the benefits often outweigh them, particularly for women with fertility challenges.
As always, it’s important to consult with a fertility specialist to determine the best course of action for your specific needs.
Disclaimer: This guide is for educational purposes and does not substitute individual medical advice. Always consult your Vrinda Fertility specialist and a registered dietitian for tailored planning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Yes, ovarian stimulation can be used for egg freezing or egg donation, not just for IVF.
Ovarian stimulation typically lasts between 10 to 14 days, depending on how the ovaries respond to the medications
Long-term risks are rare, but overuse of ovarian stimulation may affect future fertility. Always consult with your doctor for personalized advice.
The number of eggs retrieved varies by individual, but typically 8-15 eggs are retrieved during a stimulation cycle.
Expect regular monitoring through ultrasounds and blood tests, as well as hormone injections. Your doctor will provide a detailed plan for your specific situation.